Background
Rosai-Dorfman disease (RDD) is a rare heterogeneous histiocytic disorder. Because of the rarity of RDD and a lack of prospective randomized trials, the treatment strategy for RDD is mostly based on retrospective study. Previous studies showed thalidomide or lenalidomide was effective in recurrent/refractory RDD with skin involvement.
Aims
This study was designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of lenalidomide and dexamethasone (RD) for Rosai-Dorfman Disease.
Methods
This phase 2, prospective, single-center study enrolled 13 newly diagnosed and 9 recurrent patients with RDD from June 2021 to August 2022 (NCT 04924647). The RD regimen was lenalidomide 25mg d1-21 and dexamethasone 20-40mg d1,8,15,22 for a cycle and 12 cycles in total. The primary endpoint was event-free survival (EFS). Events were defined as a poor response to RD, reactivation after RD therapy or death from any cause. The secondary endpoint was overall response rate (ORR) and overall survival (OS).
Results
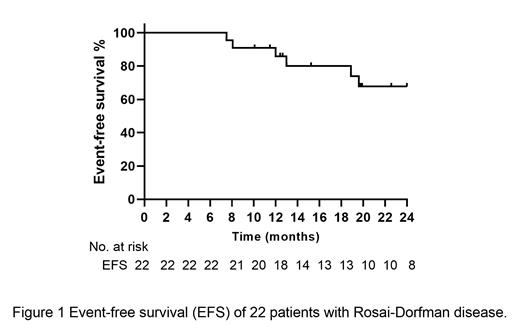
The median age was 44 years (range 21-71 years). Fifteen patients were male (68.2%). All the patients were extranodal RDD (2 unifocal, 3 single-system multifocal and 17 multisystem). The most common organ involved was bones (45.5%) and subcutaneous tissue (45.5%), followed by sinus (37.5%). Four patients (18.2%) had central nervous system (CNS) involvement. MAPK pathway alterations were found in 6/15 (20.0%) of the patients. All patients received at least six courses of RD regimen therapy, with median 12 (6-12) courses. Overall, 18 patients (81.8%) completed protocol treatment, and 4 patients (18.2%) went off protocol (3 patients' decision, 1 poor response). The overall response rate was 86.4% (19/22), including 7 patients (31.8%) achieving complete remission and 12 patients (54.5%) achieving partial remission. After a median follow-up of 22 months (range 8-24 months), 3 patients (13.6%) relapsed. No patients died or lost follow-up. The estimated 2-year EFS and OS was 67.8% and 100.0%, respectively. To evaluate the prognostic factors of EFS using univariate analysis, we found that patients with CNS, respiratory system, multi-system involvement and MAPK pathway gene mutations had similar outcomes. No patients had grade 3-4 adverse effects. 8 patients (36.4%) had grade 1 gastrointestinal complications (vomiting, nausea and diarrhea). 6 patients (27.3%) experienced anemia, neutropenia or thrombocytopenia. Only 1 patient (5.6%) had grade 2 neutropenia. 5 patients (22.7%) experienced rash and 5 patients (22.7%) experienced fatigue with grade 1 events. All complications improved with supportive treatment.
Conclusion
Lenalidomide and dexamethasone regimen is an efficient and safe regimen for newly diagnosed and recurrent RDD.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal